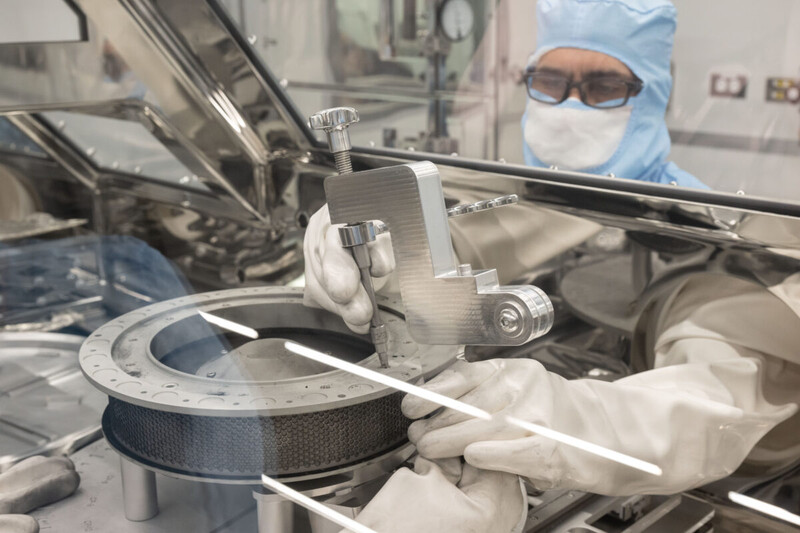
Lids get stuck. Sometimes it’s a pickle jar, and sometimes it’s a container full of dust from a 4.5 billion-year-old asteroid. That latter is what NASA faced last fall when it recovered the canister from a space rock named Bennu. NASA uses sterile environments so samples don’t get contaminated by Earth air, but none of the tools approved for the locked-down boxes could remove the final two of 35 fasteners.
All Science stories

If you don’t trust Elon Musk to stick stuff into your brain, the good news is he’s not your only option.
What happened: Musk’s Neuralink implanted its first chip into a human brain. The company has not made a formal announcement, but Musk posted on X that the recipient is “recovering well” with “promising neuron spike detection,” presumably referring to activity between the cells that send messages throughout the body.
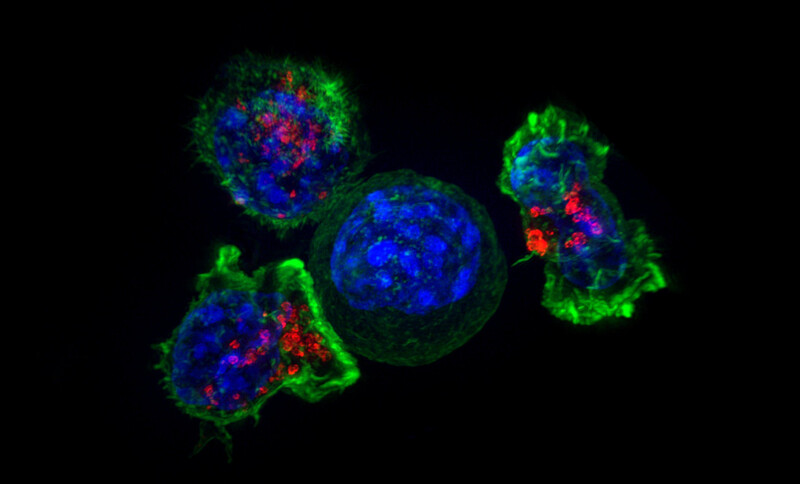
COVID-19 vaccines gave mRNA research a big boost, and scientists have been exploring how it might be used to prevent and treat other diseases. But that’s trickier when it comes to cancer: things that kill cancer cells are generally pretty bad for all cells, and your fatty tissues deliver RNA throughout your body, instead of targeting it.

Taking a page out of a vaccine developer’s playbook, a Boston biotech company is making major strides towards a breakthrough cancer treatment.
Driving the news: More than three years after the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule gained popularity for its role in COVID-19 vaccines, Strand Therapeutics will test a cancer-fighting mRNA treatment that can more precisely treat cancerous tumours, according to WIRED.
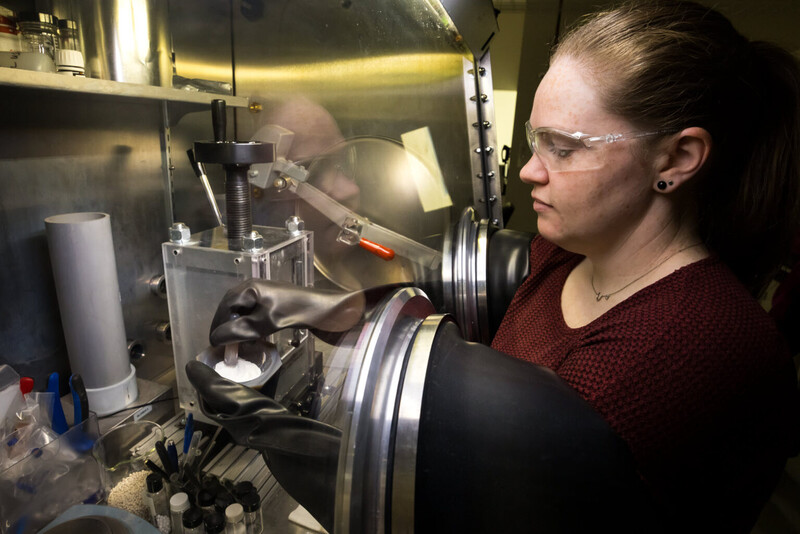

Vehicle and device batteries are driving huge demand for lithium. Since it is a non-renewable resource, scientists are looking for ways to replace or use less lithium, but with so many combinations of materials, it can be hard to know what’s worth exploring.
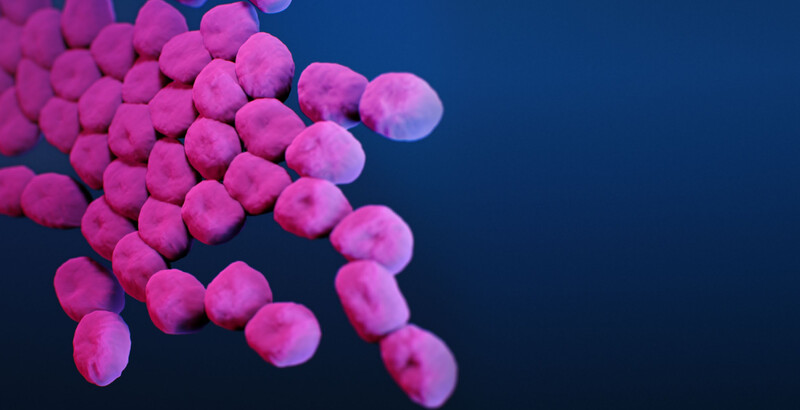
Bacteria can naturally develop antibiotic resistance, but it’s thought that a spike in these strains is caused by overuse of antibiotics, as well as misuse by patients. But a team of researchers was able to show that a new class of antibiotics was able to break through that protection.
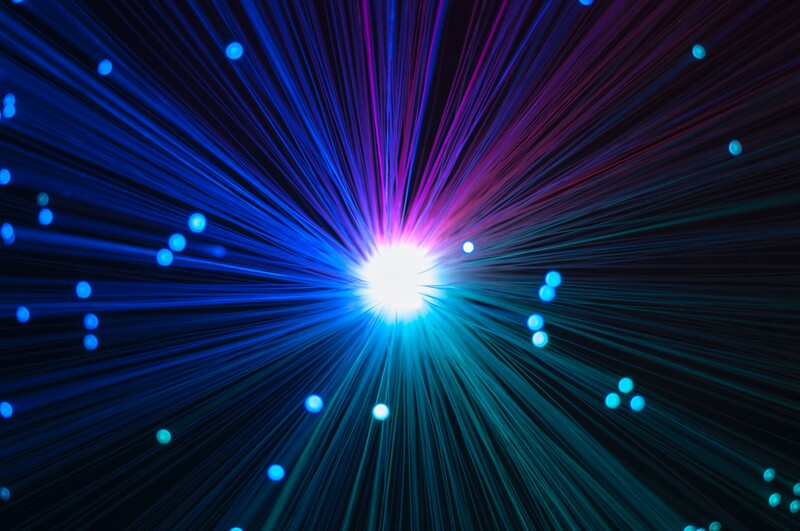
Scientists at Osaka University and UC San Diego have developed an experiment they believe could turn photons into matter using lasers.
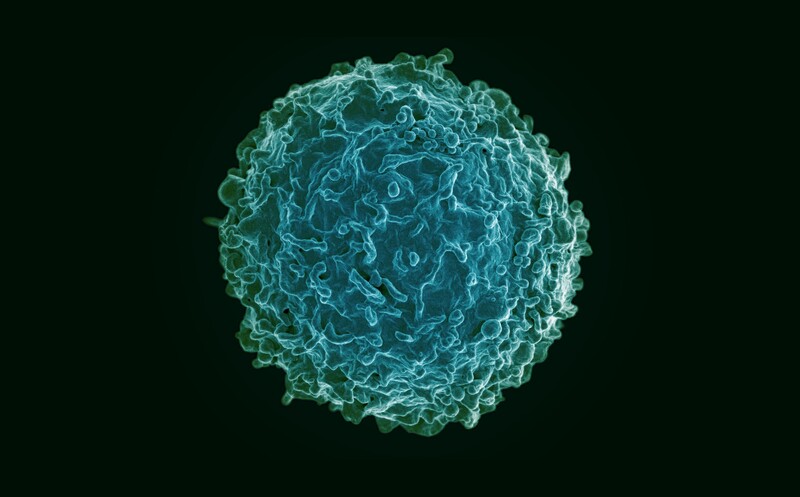
The problem: Inherited metabolic disorders happen when a defective gene creates an enzyme deficiency in the body. There are a lot of them, and some can be treated by managing diet, but others require regular enzyme infusions for a patient’s entire life.
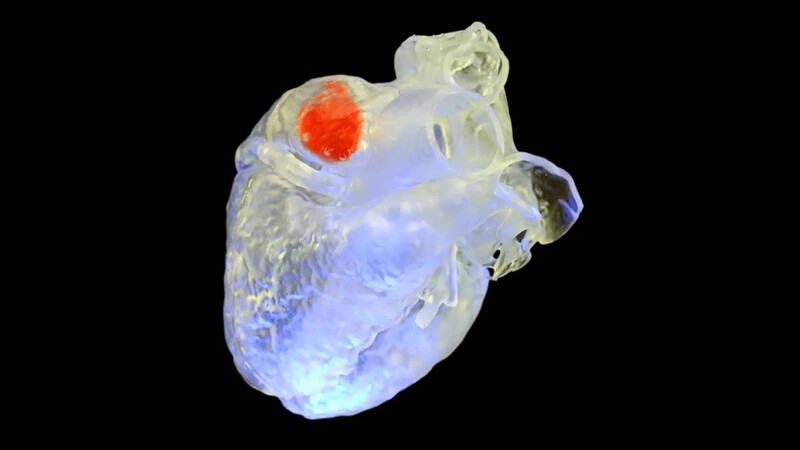
The problem: One way scientists have tried to avoid cutting people open for surgery is by injecting a photo-sensitive ink that can harden into replacement tissues, but light can’t penetrate very far through skin and organs.
The solution: Researchers at Duke University and Harvard Medical School have developed an ink that hardens when vibrated by sound waves
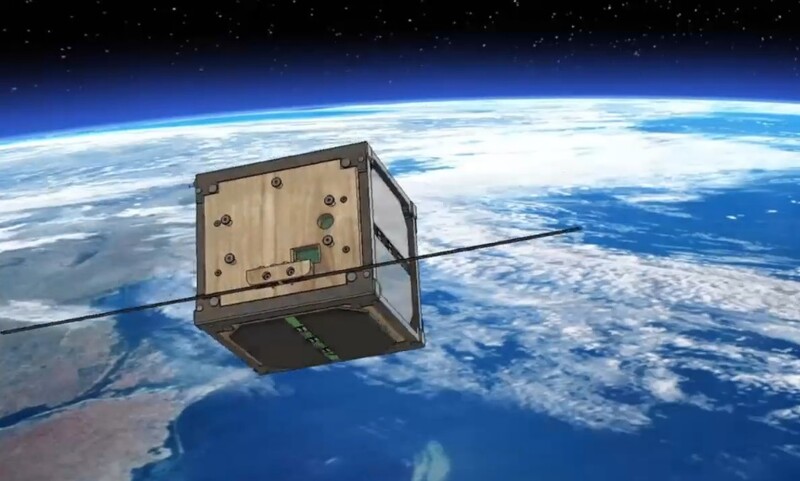

Between decommissioned satellites and bits shed from spacecraft, humans leave a lot of metal in the atmosphere. That reflective junk creates light pollution, bashes into the International Space Station, and — when it falls out of orbit and into the atmosphere — burns up into millions of tiny metallic particles.
